
작성 이유
Exception Handler 를 통한 예외 처리 작업을 하며 익혔던 예외 처리 방법을 기록하기 위해 작성하게 되었다.
Exception Handler 를 통한 예외 처리
customException 패키지에 추상 클래스인 GlobalException 과 GlobalException 클래스를 상속받는 두 개의 Custom Exception 클래스가 있다. ErrorResponse 클래스는 Exception Handler 를 통해 클라이언트로 반환하는 정보를 담고 있는 클래스.
간단한 게시글 단건 조회 Serivce 로직을 확인해보자. 이상한 게시글 아이디로 게시글을 찾는다면 IllegalArgumentException 이 발생하도록 되어있다.
@Service
public class PostService {
... 중략 ...
public PostRead read(Long postId) {
Post findPost = postRepository.findById(postId)
.orElseThrow(() -> new IllegalArgumentException("찾을 수 없는 게시글입니다."));
return PostRead.builder()
.id(findPost.getId())
.title(findPost.getTitle())
.content(findPost.getContent())
.build();
}
... 중략 ...
}
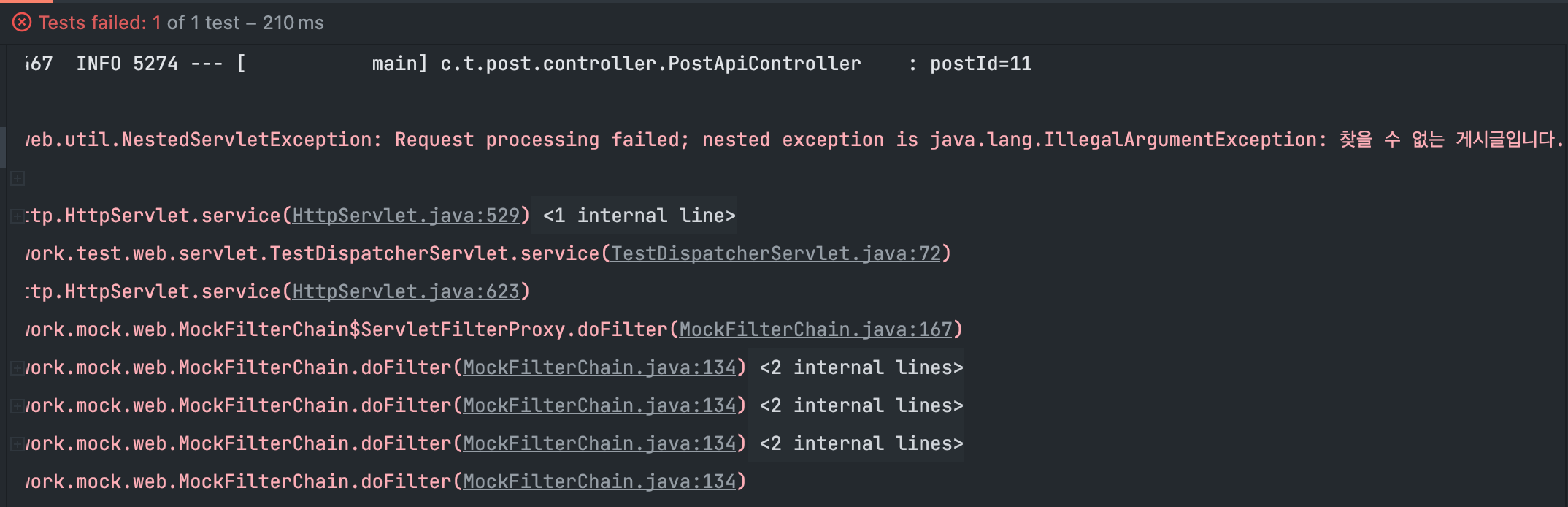
Controller 테스트를 돌려보면 서버 예외만 날 뿐 클라이언트로 보낼 마땅한 응답이 따로 생성되지 않는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
https://jeonboard.tistory.com/51 [자세한 내용은 예전 게시글 참조]
Spring @Validation 을 통한 검증, 예외처리 도전기
첫 팀 프로젝트에서 검증과 예외처리를 도전해봤는데, 엄청 중요한 내용이라고 생각해서 까먹기 전에 포스팅으로 남겨놓기 위해 글을 작성해보려고 한다 ☺️ 검증이 필요하다고 생각한 객체
jeonboard.tistory.com
@Test
@DisplayName("게시글 조회 - 존재하지 않는 게시글 조회")
void 게시글_조회_실패() throws Exception {
// given
Post post = Post.builder()
.title("title")
.content("content")
.build();
PostCreate postCreate = PostCreate.builder()
.title(post.getTitle())
.content(post.getContent())
.build();
PostRead postRead = postService.write(postCreate);
// when & then
mockMvc.perform(get("/api/posts/" + postRead.getId() + 1L)
.contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON))
.andExpect(status().isNotFound())
.andDo(print());
}
설명에 앞서 GlobalException 과 PostNotFound, InvalidRequest, ErrorResponse 클래스를 확인해보자.
보면 느끼겠지만 상수 MESSAGE, 클래스 명만 다르고 똑같은 클래스인 것을 알 수 있다. 그럼 굳이 왜 나눴는가 ? 에 대한 대답은 클래스 명만으로도 로직에서 최대한 판단할 수 있도록 하기 위함? 이라고 생각한다. 그저 IllegalArgumentException 를 Exception Handler 로 잡을 수 있지만 범위가 너무 포괄적이니까 ..
1. GlobalException
@Getter
public abstract class GlobalException extends RuntimeException {
private final Map<String, String> validation = new HashMap<>();
public GlobalException(String message) {
super(message);
}
public GlobalException(String message, Throwable cause) {
super(message, cause);
}
}
2. PostNotFound
public class PostNotFound extends GlobalException {
private static final String MESSAGE = "존재하지 않는 글입니다.";
public PostNotFound() {
super(MESSAGE);
}
public PostNotFound(Throwable cause) {
super(MESSAGE, cause);
}
}
3. InvalidRequest
public class InValidRequest extends GlobalException {
private static final String MESSAGE = "잘못된 요청입니다.";
public InValidRequest() {
super(MESSAGE);
}
public InValidRequest(Throwable cause) {
super(MESSAGE, cause);
}
}
4. ErrorResponse
@Getter
public class ErrorResponse {
private final String code;
private final String message;
@Builder
public ErrorResponse(String code, String message) {
this.code = code;
this.message = message;
}
이제 Exception Handler 를 보자. 최상위 예외 클래스인 GlobalException 을 활용했기 때문에 일괄적으로 처리할 수 있는 비슷한 Custom Excpetion 을 각각의 Handler 가 아닌 하나의 Handler 로 묶어 처리할 수 있게 되었다. 다 끝난줄 알았더니 여기서 문제 발생.
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND)
@ExceptionHandler(GlobalException.class)
public ErrorResponse globalException(GlobalException exception) {
return ErrorResponse.builder()
.code("400")
.message(exception.getMessage())
.validation(exception.getValidation())
.build();
}
Custom Exception 예외 클래스 명을 다시 생각해보자. PostNotFound, InvalidRequest ... 정말 이 둘의 Status 가 400 로 통합될 수 있을까 ? 클라이언트 예외니까 4xx 은 맞지만 정책상 PostNotFound 라면 404, InvalidRequest 라면 400 의 Status Code 를 사용해야 하지 않나 ? 이걸 수정해보자.
1. GlobalException 클래스에 추상 메서드 getStatusCode() 를 추가한다.
@Getter
public abstract class GlobalException extends RuntimeException {
public GlobalException(String message) {
super(message);
}
public GlobalException(String message, Throwable cause) {
super(message, cause);
}
public abstract int getStatusCode();
}
2. 각 구현 클래스에서 @Override 하여 getStatusCode() 를 구현한다. NotFound 는 404, InvalidRequest 는 400 으로.
public class PostNotFound extends GlobalException {
private static final String MESSAGE = "존재하지 않는 글입니다.";
public PostNotFound() {
super(MESSAGE);
}
public PostNotFound(Throwable cause) {
super(MESSAGE, cause);
}
@Override
public int getStatusCode() {
return 404;
}
}public class InValidRequest extends GlobalException {
private static final String MESSAGE = "잘못된 요청입니다.";
public InValidRequest() {
super(MESSAGE);
}
public InValidRequest(Throwable cause) {
super(MESSAGE, cause);
}
@Override
public int getStatusCode() {
return 400;
}
}
3. Exception Handler 를 수정한다.
- 각 예외 클래스에 맞게 Status Code 를 내려주기 위해 @ResponseStatus 어노테이션 삭제
- ResponseEntity<> 를 활용해 가져온 Status Code 를 인자로 넣어주는 형태로 ErrorResponse 를 감싸서 반환하도록 수정
@ExceptionHandler(GlobalException.class)
public ResponseEntity<ErrorResponse> globalException(GlobalException exception) {
int statusCode = exception.getStatusCode();
ErrorResponse errorResponse = ErrorResponse.builder()
.code(String.valueOf(statusCode))
.message(exception.getMessage())
.build();
return ResponseEntity.status(statusCode).body(errorResponse);
}
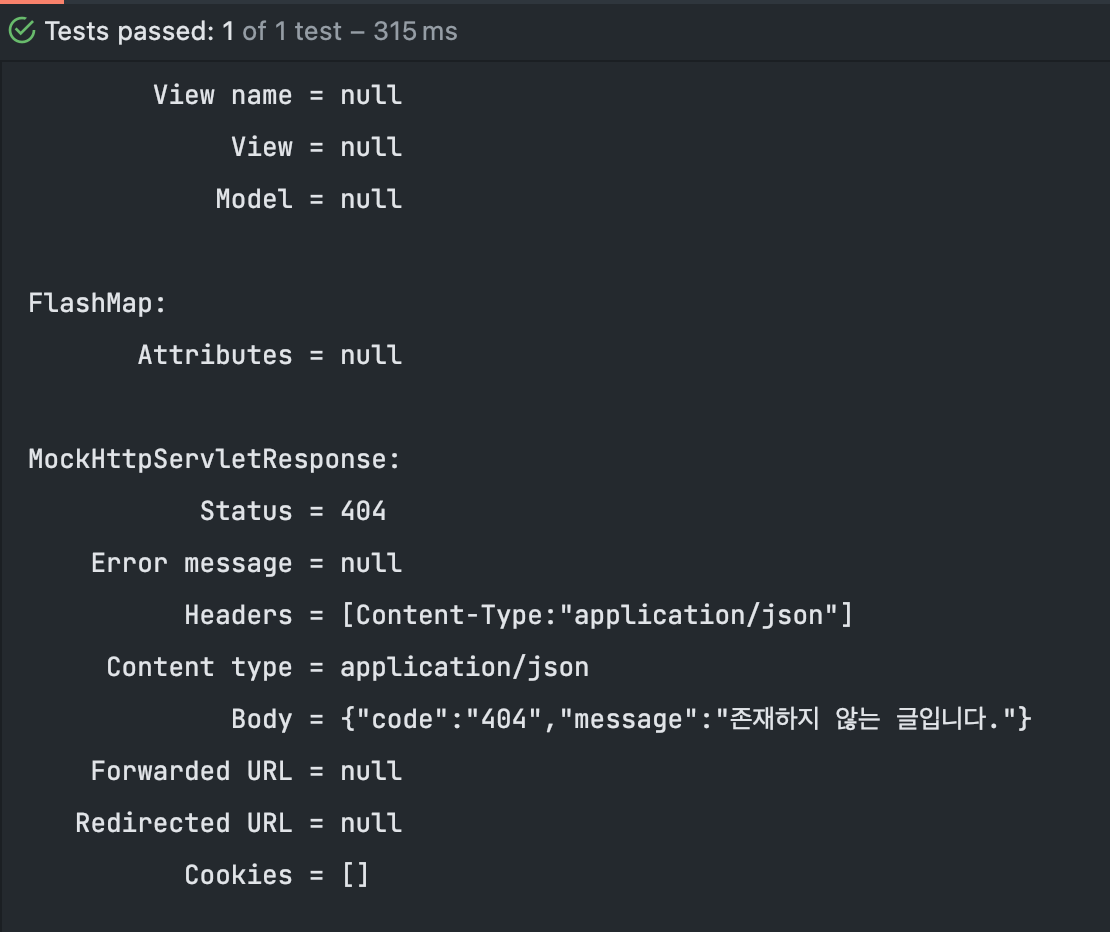
자 그럼 Exception Handler 도 수정했으니 Service 의 orElseThrow() 를 수정하고 테스트를 돌려보면 원하는 JSON 형태로 응답이 내려가는 모습을 확인할 수 있다.
@Service
public class PostService {
... 중략 ...
public PostRead read(Long postId) {
Post findPost = postRepository.findById(postId)
.orElseThrow(PostNotFound::new);
return PostRead.builder()
.id(findPost.getId())
.title(findPost.getTitle())
.content(findPost.getContent())
.build();
}
... 중략 ...
}
사실 이 글을 작성한 이유는 이제부터 시작이다. PostNotFound 와 같은 예외는 클래스 명으로 바로 파악이 가능할 만큼 직관적인 예외다. 그러니까 따로 어떤 필드에서 무슨 예외가 터졌는지 굳이 알 필요가 없다는 뜻. ("존재하지 않는 게시글을 요청했다면 그 게시글 번호를 보내주세요!" 와 같은 클라이언트 요청이 없다는 가정하에)
그에비해 InvalidRequest 클래스를 봤을 때는 한번에 파악하기 힘들고 어떤 필드로 어떤 잘못된 요청이 왔는지 클라이언트로 보내주고 싶은데 어떻게 해야할까 ? 예를 들어서, Title 값에 "바보" 라는 값이 있다면 InvalidRequest 예외를 잡아주는 것으로 예시를 들어보자. 이런건 스프링 validation 에서 제공하는 NotEmpty 등으로는 잡아낼 수 없다.
1. Service 단으로 들어갈 필요도 없을 듯해서 그냥 Controller 에서 바로 검증 메서드 호출
@PostMapping("/api/posts")
public PostRead post(@RequestBody @Valid PostCreate postCreate) {
log.info("postRequest={}", postCreate.toString());
postCreate.validate();
return postService.write(postCreate);
}
2. PostCreate 값을 Controller 에 꺼내서 검증하는 건 객체지향적으로 지양해야하는 방법. 메세지를 보내기 위해 validation() 추가하고 Title 값에 "바보" 가 존재한다면 Custom Exception 인 InvalidRequest 예외 클래스가 호출되도록 한다. 인자로 어떤 필드, 어떤 잘못된 요청이 왔는지 함께 보내준다.
@NoArgsConstructor
@Getter
public class PostCreate {
...중략
public void validate() {
if (title.contains("바보")) {
throw new InValidRequest("title", "제목에 바보를 포함할 수 없습니다.");
}
}
}
3. FieldName, Message 를 받아 InvalidRequest 를 생성함과 동시에 GlobalException 의 addValidation() 을 호출하면서 GlobalException 필드 값을 채워주도록 한다. 4번 코드 참고
public class InValidRequest extends GlobalException {
private static final String MESSAGE = "잘못된 요청입니다.";
public InValidRequest() {
super(MESSAGE);
}
// InValidRequest 생성 시점에 fieldName, message 삽입
public InValidRequest(String fieldName, String message) {
super(MESSAGE);
addValidation(fieldName, message);
}
@Override
public int getStatusCode() {
return 400;
}
}
4. 최종 GlobalException 클래스
Map 으로 충분히 아름답게 응답할 수 있다고 생각해 다른 Response 클래스를 생성하지 않고 Map Type 으로 validation 변수를 초기화한 뒤 InvalidRequest 클래스가 생성됨과 동시에 모든 응답 값 셋팅이 완료된다.
@Getter
public abstract class GlobalException extends RuntimeException {
private final Map<String, String> validation = new HashMap<>();
public GlobalException(String message) {
super(message);
}
public GlobalException(String message, Throwable cause) {
super(message, cause);
}
public abstract int getStatusCode();
public void addValidation(String fieldName, String message) {
validation.put(fieldName, message);
}
}
5. 이제 GlobalException 클래스에 셋팅된 Map Type 의 validation 필드를 응답 클래스인 ErrorResponse 에 넘겨줄 수 있게 되었다. 그 전에 ErrorResponse 필드로 Map Type validation 필드를 만들어주고, Exception Handler 에서 validation 을 넣어주면 응답 객체도 생성 완료 !
@Getter
public class ErrorResponse {
private final String code;
private final String message;
private final Map<String, String> validation;
@Builder
public ErrorResponse(String code, String message, Map<String, String> validation) {
this.code = code;
this.message = message;
this.validation = validation;
}@ExceptionHandler(GlobalException.class)
public ResponseEntity<ErrorResponse> globalException(GlobalException exception) {
int statusCode = exception.getStatusCode();
ErrorResponse errorResponse = ErrorResponse.builder()
.code(String.valueOf(statusCode))
.message(exception.getMessage())
.validation(exception.getValidation())
.build();
return ResponseEntity.status(statusCode)
.body(errorResponse);
}
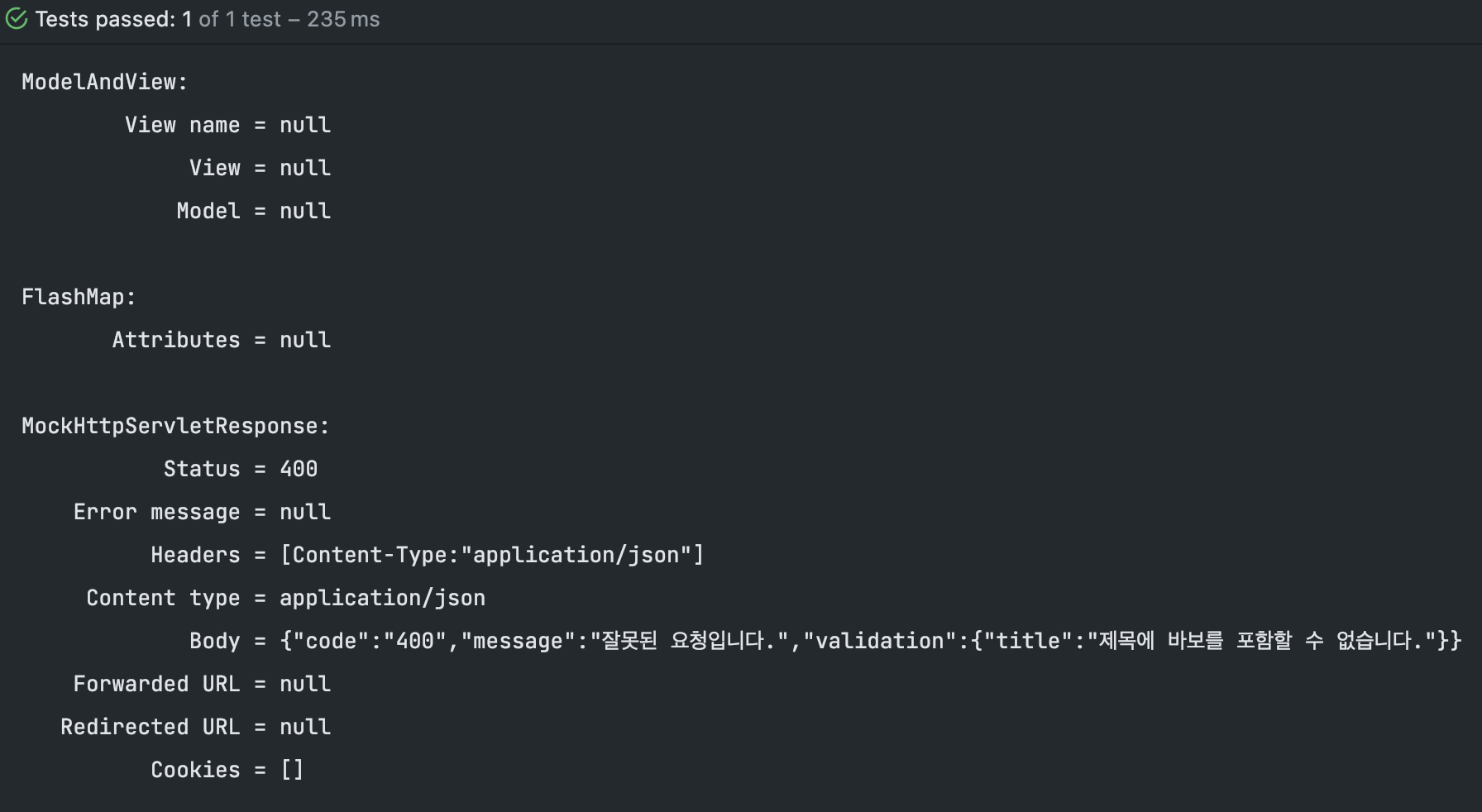
6. Test 결과를 확인하면 ?
@Test
@DisplayName("게시글 작성 - 제목에 '바보' 는 포함될 수 없다.")
void 게시글_생성_실패_제목_검증() throws Exception {
// given
PostCreate postCreate = PostCreate.builder()
.title("나는 바보입니다.")
.content("content")
.build();
mockMvc.perform(post("/api/posts")
.contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
.content(mapper.writeValueAsString(postCreate)))
.andExpect(status().isBadRequest())
.andDo(print());
}
'SPRING' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Spring Security] Authentication 인증 처리 과정 알아보기 (0) | 2022.12.17 |
|---|---|
| DTO 반환에 대해 (4) | 2022.10.13 |
| [Spring] GitHub OAuth2.0 구현하기 (웹 버전) (2) | 2022.05.23 |
| Spring @Validation 을 통한 검증, 예외처리 도전기 (0) | 2022.04.16 |
